How AI Is Transforming Trade Compliance
1. How AI is Transforming Trade Compliance: Key Takeaways
- Trade compliance ensures that goods cross borders legally and ethically by following international rules, sanctions, tariffs, and customs requirements. It governs what can be traded, with whom, and under what conditions, making it a critical part of global business operations.
- Global trade companies face five major hurdles: ever-changing regulations, complex export control laws, hidden risks in supply chains, disruptions from geopolitical tensions, and a lack of automation in compliance processes. These factors make compliance costly, time-consuming, and error-prone.
- AI helps businesses overcome these challenges by automating data analysis, improving supply chain transparency, enabling real-time collaboration, keeping pace with tariff and HS code changes, and streamlining ESG reporting. With AI, compliance becomes faster, more accurate, and more strategic, turning a traditional burden into a competitive advantage.
2. Current Challenges of Trade Compliance
Trade compliance is becoming one of the toughest areas for global businesses to manage. The rules that govern what can be traded, with whom, and under what conditions are changing faster than many companies can keep up. Below are five of the most pressing challenges businesses face today — and why they matter.
2.1. Challenge One: Ever-Changing Regulations
One of the hardest realities of global trade is that the rules never stay the same. Governments introduce new sanctions, tariffs, and export restrictions with little warning, leaving companies scrambling to stay compliant.
Take the U.S. as an example.
In late 2024, the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) rolled out a new 10-year recordkeeping requirement— forcing businesses to hold compliance records for much longer than before. At the same time, the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) added new names to its “Trade Integrity” watchlist, instantly expanding the number of restricted parties.
The cost of falling behind is steep.
A Thailand-based company was fined $20 million by OFAC for hundreds of violations tied to Iran. Cases like this underline a simple truth: unless companies constantly update training, invest in compliance technology, and educate their staff, they risk penalties that can wipe out years of profits.
2.2. Challenge Two: Navigating Complex Export Control Laws
Export control laws are designed to keep sensitive goods out of the wrong hands — but for companies, they can be a legal maze. The complexity grows with dual-use goods, products that can serve both civilian and military purposes. Misclassifying these goods or overlooking license requirements can lead to massive penalties.
For example, a U.S. electronics manufacturer paid $5.8 million in fines in 2024 for exporting restricted components linked to China’s military. In an even bigger case, a major defense contractor settled violations of the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) for a staggering $200 million.
These cases show how risky it is to rely only on manual checks or guesswork. To avoid costly mistakes, businesses need strong product classification systems and automated license-checking tools that can flag issues before shipments leave the warehouse.
2.3. Challenge Three: Managing Supply Chain Risks
Modern supply chains are vast and interconnected, making it incredibly difficult for companies to know exactly who they’re dealing with. A business might think it is trading with a trusted partner, but that partner may be sourcing goods or services from sanctioned or blacklisted entities further down the chain.
The EU recently fined companies for bypassing sanctions on Russia by routing trade through intermediaries in Turkey and Kazakhstan. Similarly, under the U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), customs authorities detained $1.73 billion worth of goods in 2024 that were suspected of links to forced labor.
To protect themselves, companies must conduct thorough supplier audits, run third-party risk checks, and adopt advanced screening technologies that can dig deeper than surface-level vetting. Without these safeguards, they face both financial penalties and reputational damage.
2.4. Challenge Four: Trade Disruptions from Geopolitical Tensions
Politics and conflict often reshape trade overnight, and compliance teams are left to deal with the fallout. The ongoing U.S.-China trade dispute, for instance, has forced many companies to diversify operations under a “China+1” strategy to reduce exposure to tariffs and restrictions.
Other global conflicts have had even harsher consequences. The war in Ukraine triggered unprecedented sanctions against Russia, forcing over 1,000 Western companies to reduce or stop operations there entirely. Such geopolitical shocks illustrate why compliance is not just about following existing rules but also about preparing for sudden changes that can disrupt supply chains, markets, and customer bases.
The lesson here is clear: companies need to build geopolitical risk assessments into their business strategies. By doing so, they can act quickly, adapt to sanctions or tariffs, and keep disruptions to a minimum.
2.5. Challenge Five: Lack of Automation in Compliance Processes
Despite the complexity of global trade, many companies still manage compliance with basic tools like spreadsheets and email. This manual approach is slow, prone to mistakes, and simply not up to the task of monitoring thousands of shipments, regulations, and counterparties in real time.
Until now, compliance software hasn't widely implied among companies. That means the vast majority are exposing themselves to unnecessary risk. On the other hand, leading organizations are turning to automation and AI to streamline their compliance processes.
Technologies like machine learning can monitor regulations in real time, automatically flag suspicious transactions, and reduce human error. Automated systems also make compliance scalable — allowing a company to handle growth without multiplying its compliance team. For global players, investing in automation is no longer optional; it’s becoming the minimum standard for staying competitive and compliant.
3. How AI is Transforming Trade Compliance
Global trade companies face nonstop regulatory changes and massive data flows that are hard to manage manually. Yet, AI provides solutions by cutting through this complexity. Let's discover how AI is transforming trade compliance.
3.1. Data Automation & Analysis
AI is making the biggest impact in trade compliance through data analysis and automation. Every day, global trade creates enormous amounts of data: customs forms, invoices, shipping records, supplier details, and new regulations from different governments. Manually handling all of this is slow and full of mistakes. AI changes that by processing data in real time, spotting errors, and keeping compliance systems automatically updated.
This directly helps solve two major challenges:
- Constantly changing regulations – AI tools can track new sanctions, tariffs, or export rules and update company systems instantly, so businesses don’t fall behind.
- Lack of automation – instead of using spreadsheets or emails, AI automates tasks, reducing human error and saving valuable time.
A good example is denied party screening (DPS).
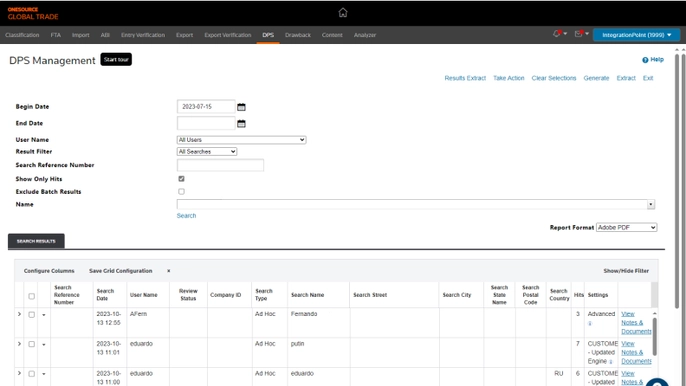 \
\
Normally, compliance staff have to check customer and supplier names against sanctions lists, often wasting hours on false matches. AI can automate this process, quickly clearing safe names and only passing suspicious ones for human review. This gives compliance officers more time to focus on real issues.
Moreover, AI also allows for customization. Companies can set how strict the system should be, depending on their risk. For example, a defense company may want very sensitive screening, while a consumer goods exporter may choose a lighter approach.
Other uses include analyzing trade documents for missing details, monitoring global regulations, assessing partner risks, and mapping supply chains for hidden links to restricted entities.
However, be aware that there are always two sides to a story. AI isn’t perfect, trade rules can be complex, and poor-quality data can still cause mistakes. That’s why human oversight is essential. But for global trade companies, AI-powered data analysis and automation are quickly becoming the only way to manage compliance efficiently at scale.
Data analysis and automation show how powerful AI can be in cutting through the complexity of trade compliance. But for global trade companies, the real advantage comes from using AI not just to process data, but to connect the dots across entire supply chains and regulations in real time.
That’s exactly what yTrade delivers — an AI-powered platform that keeps sanctions and policies current, makes customs data instantly accessible, and turns billions of trade records into clear, actionable insights.
With yTrade, compliance stops being a burden and becomes a tool to move faster, smarter, and with confidence in any market. Discover our AI-powered trade data center now!
3.2. Supply Chain Transparency & Risk Management
One of the most pressing compliance challenges for multinational traders is supply chain opacity. With complex, multi-tier supplier networks and multiple intermediaries involved in cross-border transactions, companies often lack end-to-end visibility into their counterparties. This creates material risk exposure, from inadvertent dealings with sanctioned entities to violations under forced labor regulations such as the U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA).
AI is reshaping how companies approach this problem by delivering real-time transparency across the value chain. Instead of relying on static supplier declarations or manual audits, AI engines continuously aggregate and analyze vast datasets, including shipment records, trade filings, sanction lists, and partner networks, to surface potential compliance gaps.
Key applications for global trade companies include:
- Entity resolution and risk detection – AI cross-references counterparties against global watchlists and regulatory databases, flagging sanctioned or high-risk entities across multiple jurisdictions.
- Predictive disruption analysis – algorithms leverage historical trade flows, weather models, and geopolitical indicators to anticipate bottlenecks and recommend contingency routing.
- Operational optimization – advanced analytics optimize shipping routes, reduce dwell times, and improve fuel efficiency while ensuring transactions remain within compliance parameters.
For example, if geopolitical tensions escalate in a critical maritime corridor, AI systems can proactively flag the risk, model potential disruption scenarios, and recommend alternate sourcing or routing strategies. This transforms compliance from a reactive reporting function into a proactive risk management capability.
Beyond compliance, AI-driven supply chain visibility enhances resilience and competitiveness. Companies can validate supplier integrity, monitor ESG compliance, and ensure cross-border operations are aligned with international regulations in near real time.
In a global environment where one non-compliant node can compromise the entire network, AI-enabled supply chain transparency is becoming a strategic necessity rather than a compliance add-on.
3.3. Real-time Data Sharing & Collaboration
In global trade, compliance is all about coordination.
Goods cross multiple borders, involving customs authorities, logistics providers, suppliers, and regulators. Without smooth collaboration, even one gap in communication can create delays, penalties, or compliance breaches.
AI is solving this by enabling real-time data sharing and collaboration across the trade ecosystem. Instead of relying on emails, spreadsheets, and disconnected systems, AI-powered platforms bring everyone into a single digital space where compliance data, shipment status, and regulatory updates are shared instantly.
For example:
- Customs coordination – AI-enabled platforms allow customs agencies to exchange data in real time, speeding up border clearance and reducing bottlenecks. This is especially critical for time-sensitive goods like fresh produce or pharmaceuticals.
- Centralized compliance management – companies can submit declarations, monitor regulatory updates, and track compliance obligations in one unified system, cutting down on manual tasks.
- Fewer false positives – AI filters out low-quality hits during screening, reducing manual review fatigue and minimizing human error.
By connecting stakeholders, AI transforms compliance from a series of isolated tasks into a collaborative, automated process. Trade partners can monitor compliance status together, adapt instantly to new rules, and coordinate shipment flows without duplication or delays.
This directly addresses the lack of automation challenge. Instead of compliance teams drowning in repetitive manual checks, AI reduces noise, handles routine processes, and ensures that global trade partners are aligned in real time. The result is not just faster operations, but a compliance process that is more accurate, transparent, and resilient.
3.4. Keeping Up with Tariff Changes
Tariffs are one of the most unpredictable and costly aspects of global trade. A sudden change in tariff rates can reshape the cost structure of imported goods overnight, forcing businesses to rethink sourcing strategies, adjust pricing, and rework supply chains just to stay competitive. For global trade companies, the ability to track these changes in real time is no longer optional — it’s essential.
AI provides a powerful solution by automating the monitoring and interpretation of tariff updates. Instead of relying on manual checks or outdated spreadsheets, AI-driven platforms continuously scan regulatory announcements, trade agreements, and customs databases to flag changes the moment they occur. This allows businesses to respond immediately, whether that means recalculating landed costs, updating documentation, or shifting sourcing to lower-cost markets.
Key applications include:
- HS code classification – AI eliminates the guesswork in assigning Harmonised System codes, reducing misclassification risks that often lead to fines, delays, or even cargo seizures.
- Automated recalculations – tariffs and duties are updated in real time within customs management systems, helping companies maintain accurate landed cost models.
- Strategic sourcing decisions – AI insights help companies evaluate alternative suppliers or markets when tariff changes impact profitability.
Consider the example of Michael, a UK-based exporter of artisan goods. Repeated misclassification of products led to costly delays and penalties. With AI-powered classification, he could assign the correct HS codes instantly, avoid fines, and move shipments smoothly across borders.
This is how AI directly addresses the challenge of navigating complex export control laws. By ensuring goods are classified accurately, documentation is updated automatically, and tariff shifts are flagged in real time, businesses can stay compliant while protecting profitability.
3.5. AI-Enabled ESG Monitoring
Global trade today demands not only the movement of goods across borders but also proof that supply chains are ethical, sustainable, and transparent. Many countries now enforce Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria when deciding which businesses they will trade with. For international companies, this means supply chains must meet standards around sustainability, fair labor, and responsible sourcing — or risk being excluded from markets.
AI is playing a growing role in helping businesses meet these ESG requirements by automating the collection, validation, and reporting of compliance data. Instead of ESG teams spending weeks compiling reports from scattered sources, AI can scan large volumes of trade, supplier, and regulatory data in minutes, ensuring accuracy and consistency across the board.
Key benefits for global trade companies include:
- Efficiency – AI automates repetitive ESG tasks such as data collection, gap analysis, and report preparation, reducing time spent on manual work.
- Accuracy – by cross-referencing data points and standardizing inputs, AI minimizes errors and ensures compliance with complex ESG frameworks.
- Scalability – AI can process thousands of supplier records or ESG disclosures at once, helping companies respond quickly to regulatory audits or new reporting demands.
- Continuity – AI systems provide a steady flow of updated insights, ensuring ESG strategies remain aligned with evolving global standards.
For example, exporters often struggle with accurate reporting on forced labor risks or carbon footprints across multi-tier supply chains. AI-driven platforms can flag anomalies, validate supplier declarations, and ensure documentation aligns with regulatory expectations. This reduces legal, financial, and reputational risks while also building trust with investors, regulators, and customers.
Of course, AI is not a replacement for human oversight. Domain expertise is still critical to interpret grey areas and ensure ESG reports align with both regulations and stakeholder expectations. But with the right tools in place, companies can turn ESG compliance from a regulatory burden into a competitive differentiator — showing global partners and markets that their supply chains are not just compliant, but also ethical and future-ready.
4. Conclusion
When it comes to trade compliance, every shipment, every supplier, and every tariff shift matters. Regulations can change overnight, export controls are increasingly complex, and unseen supply chain risks can lead to multimillion-dollar penalties. So, how is AI transforming trade compliance? By shifting it from a costly burden into a strategic advantage — powering data automation, supply chain risk management, real-time market updates, ESG monitoring, and more for global trade companies.
That advantage is exactly what yTrade delivers. With AI-powered supply chain mapping, real-time compliance, and risk insights, yTrade equips businesses to navigate sanctions, manage HS codes, and access customs data worldwide with speed and confidence.
